
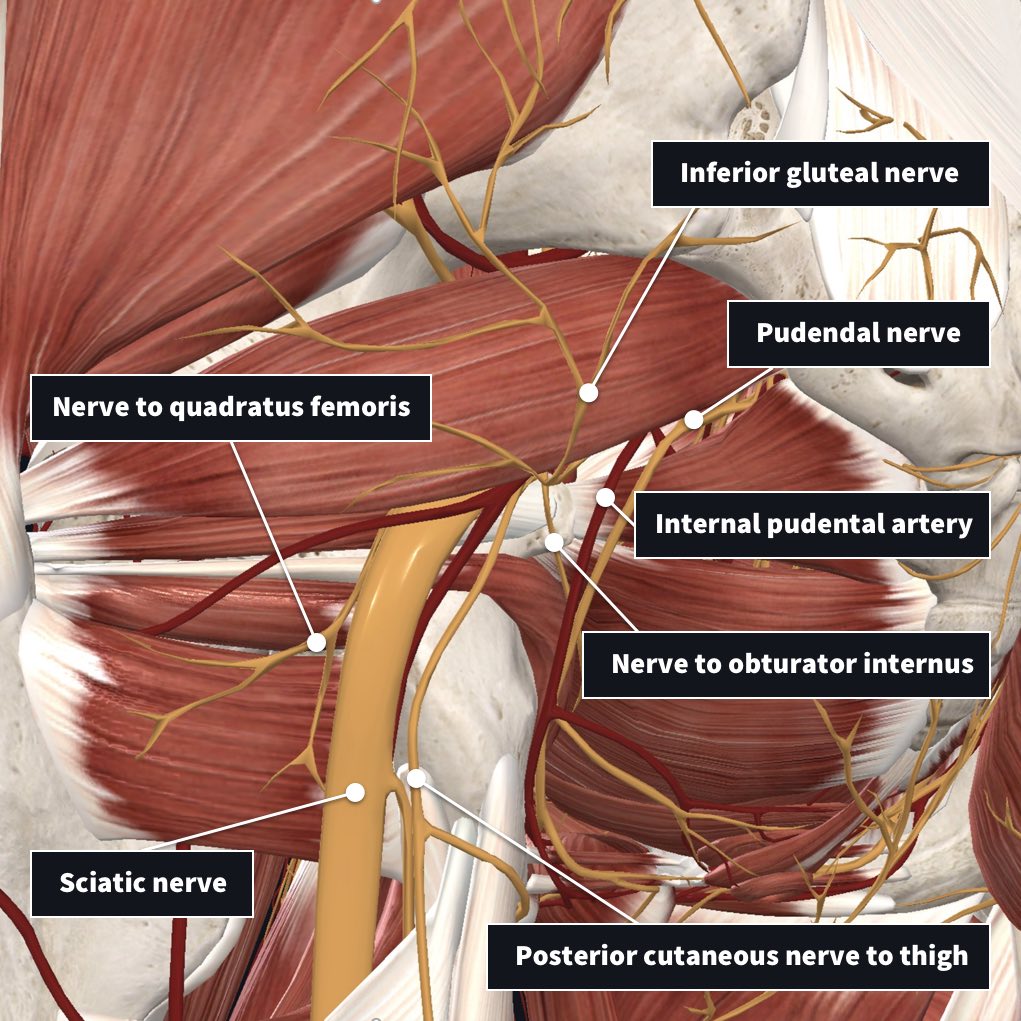
It eventually emerges from under the tendon of brachioradialis proximal to the radial styloid and passes over the anatomical snuffbox. At the same time, you get to navigate between various layers and understand the connection between muscles, nerves, bone parts, insertions points, and so on. It lies from above downwards on supinator, pronator teres and flexor digitorum superficialis and is posterior to brachioradialis. Complete Anatomy 2020 allows you to see the full-body, or only the head and neck, upper or lower limbs, thorax, abdomen, back, or pelvis. action: elevation (shortens as mouth closes) innervation: trigeminal. The superficial branch courses towards the wrist lateral to the radial artery (which runs with it one third of the way down the forearm) and enters the hand, dividing into the dorsal digital cutaneous branches. insertion: coronoid process and ramus of mandible. The complete Skeletal System and a few other contents are. It enters the cubital fossa, where it divides into superficial and deep branches. This video Upper Limb: Superficial Structures & Cutaneous Innervations is part of the Lecturio course Anatomy WATCH the complete course on http://lectu. This app is freely downloadable, however in-app purchase is required to unlock the contents. It passes to the forearm by coursing anterior to the lateral epicondyle at the level of the elbow joint. It lies deep to the upper brachialis and then brachioradialis. It pierces the lateral intermuscular septum at the midpoint of the humerus to enter the anterior compartment of the arm. In the posterior compartment of the arm, it winds its way around the spiral groove of the humerus, accompanying profunda brachii artery. The radial nerve lies posterior to the axillary artery in the axilla and enters the posterior compartment of the arm under teres major muscle via the triangular interval. It receives contributions from C5-T1 nerve roots.
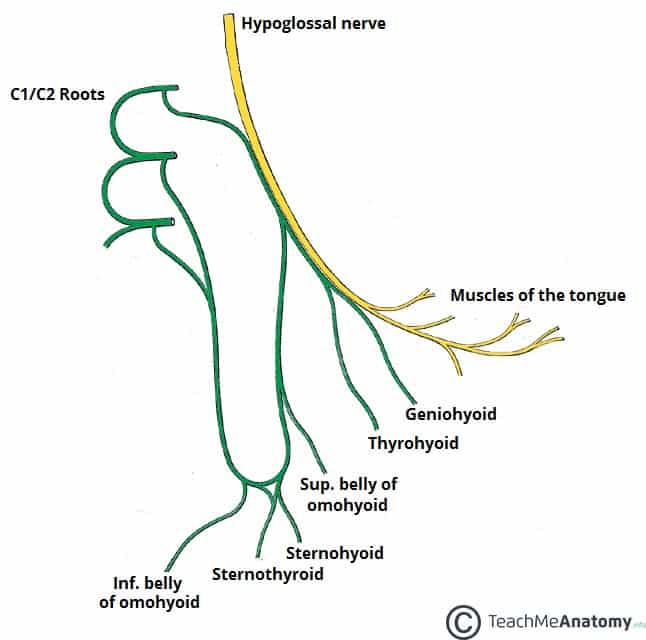
The radial nerve is one of two terminal branches of the posterior cord of the brachial plexus. sensory: dorsal aspect of the thumb, index and middle fingers.motor: elbow, wrist and finger extension.See detailed information for each skeletal muscle: blood supply, innervation. terminal branches: posterior interosseous (deep) and superficial radial nerves Learn more about muscles, bones, and their injuries with our detailed.course: posteromedially with the axillary vessels, behind the humerus, then anteriorly towards the elbow where it divides into superficial and deep branches.origin: one of two terminal branches of the posterior cord of the brachial plexus.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
